Electric cars are the wave of the future for transportation. These revolutionary vehicles are powered by electricity instead of relying on fossil fuels and are becoming increasingly popular and affordable. But how do electric cars actually work? In this article, we’ll explore the mechanics behind this amazing technology and break down the different components that make electric cars run.
short table explaining how electric cars work
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Electric Motor | Converts electricity to motion. |
| Battery | Stores and supplies power. |
| Controller | Regulates power to the motor. |
Electric cars use an electric motor powered by a battery, controlled by a controller to propel the vehicle.
The Basics of Electric Cars
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular. They are more efficient, cost less to run, and they produce no emissions – making them much better for the environment. But how do electric cars actually work? Batteries power electric cars.
The batteries store electricity, which is then used to power the electric motor. This is why electric cars are also known as battery electric vehicles (BEVs). The electric motor is connected to the wheels and propels the car forward.
When the accelerator pedal is pressed, the motor spins, turning the axle and driving the wheels. The battery itself is made up of many individual cells. Most electric cars use lithium-ion batteries, which are often found in other consumer electronics like laptops and cell phones.
The cells are connected to form a battery pack, which is then connected to the electric motor. The battery pack is recharged by plugging the car into an electric outlet. The battery pack can be recharged overnight or in a few hours, depending on the size of the battery pack.
Some cars even have the option to be recharged at public charging stations, which are becoming increasingly common. The electric motor is much more efficient than the internal combustion engine found in most cars. This is because electric motors are able to convert more of the energy stored in the battery into motion.
Electric motors also require less maintenance than combustion engines, as they have fewer moving parts. Overall, electric cars are becoming more popular due to their efficiency and environmental friendliness. They are powered by batteries, which are recharged by plugging into an electric outlet.

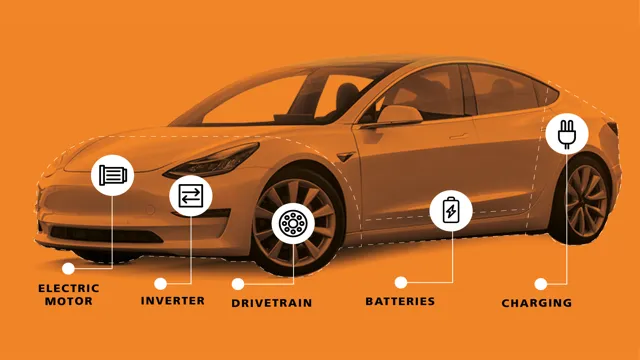
Parts of an Electric Car
Have you ever wondered how an electric car works? While it may seem like an intimidating concept, understanding the parts that make up an electric car can help demystify the process. Electric cars contain a few key components, including an electric motor, batteries, a controller, and a charging port. The electric motor is the primary source of power in the car and the batteries power it.
The controller manages the flow of electricity from the battery to the motor and ensures that the motor runs efficiently. Finally, the charging port allows the car to be recharged when needed. All of these parts work together to create the power needed to drive the electric car.
Advantages of Electric Cars
Electric cars are becoming more and more popular with each passing day, and for good reason. Not only are they eco-friendly and efficient, they also offer a number of other advantages that make them a great choice for many people. But how do electric cars actually work? In short, electric cars are powered by an electric motor that draws power from rechargeable batteries.
These batteries are then charged by plugging the car into an electric outlet or via regenerative braking, which converts the energy from braking into electricity. This electricity is then used to power the car’s motor and other electrical components. Electric cars are typically much more efficient than their gas-powered counterparts, resulting in less fuel costs and emissions.
Additionally, electric cars require very little maintenance, making them a cost-effective choice in the long run.
The Science Behind Electric Cars
Electric cars are quickly becoming the vehicle of choice for many drivers who are looking for an environmentally friendly and cost-saving alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. But what exactly is the science behind electric cars? How do electric cars work and what makes them a better option than gasoline-powered vehicles? At the heart of every electric car is a rechargeable battery. This battery stores and releases energy, which is then used to power the car’s motor.
Most electric cars today use lithium-ion batteries, which are known for their high energy density, long cycle life, and low self-discharge rate. These batteries are very efficient and can store a large amount of energy, which allows them to be used in electric vehicles. The motor in an electric car is powered by the energy stored in the battery and is usually an electric motor or a combination of an electric motor and an internal combustion engine.
The motor is connected to the drivetrain, which is a system of gears and other components that convert the motor’s power into movement. The drivetrain allows the motor to spin a wheel, which turns the car and propels it forward. Electric cars are also equipped with an electronic controller, which is a device that regulates the power output of the motor.
The controller adjusts the speed of the motor based on the amount of energy stored in the battery and the amount of power being requested from the driver. This allows the driver to accelerate or decelerate as needed. Electric cars also feature regenerative braking, which helps to recharge the battery.
When the driver applies the brakes, the motor works in reverse and converts the energy from the brakes into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This helps to extend the range of the vehicle and makes it more efficient. Electric cars are a great option for drivers who want to reduce their carbon footprint and save money on fuel costs.
They have many advantages over gasoline-powered vehicles and are becoming increasingly popular as the technology behind them continues to improve. With the right knowledge and understanding of how electric cars work, you can make an informed decision about whether or not they are the right choice for you.

The Battery
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular as the technology continues to improve and become more widely available. But how do electric cars actually work? How do they store and use electricity to travel? To better understand how electric cars work, let’s take a look at the key components of the technology. At the heart of an electric car is a battery.
This battery is responsible for storing and releasing energy to power the car’s motor. Most electric cars use lithium-ion batteries, which are lightweight and efficient. The battery is connected to an electric motor, which is responsible for turning the energy stored in the battery into the power needed to move the car.
The electric motor then powers the car’s wheels, allowing the car to accelerate, brake, and turn. The battery powers the motor, but the car also needs a way to recharge the battery to keep it running. The majority of electric cars use regenerative braking, which captures energy from the car’s brakes and converts it into electricity to recharge the battery.
So there you have it! Electric cars use their battery, electric motor, and regenerative braking system to store, convert, and recharge energy to power the car’s movement. By harnessing the power of electricity, electric cars are now a viable option for commuters everywhere.
The Motor
We all know the traditional combustion engine of our beloved gasoline-powered cars, but how do electric cars work? A combination of batteries, electric motors, and controllers powers electric cars. The batteries are charged by plugging the car into an electric outlet or charger, and the electric motor is powered by the electricity stored in the battery. The controller regulates the amount of power sent to the motor, allowing the driver to control the speed and power of the car.
Additionally, the regenerative braking system in electric cars captures the energy generated from braking and uses it to recharge the car’s batteries. With the combination of these components, electric cars are able to provide a smooth, efficient, and ultimately eco-friendly driving experience.
The Charging System
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular due to their eco-friendly nature and the convenience of charging. But how do electric cars work? It’s a fascinating system with many components that ultimately power the vehicle. To put it simply, electric cars use electricity stored in batteries to power an electric motor, which then turns the axles to move the vehicle.
The electricity is drawn from the batteries, which are recharged by connecting the car to an external power source, such as a home wall outlet or a public charging station. The process of recharging the batteries can take anywhere from a few hours to several days, depending on the size of the battery and the type of charger. The electricity is then converted into motion through the motor, which turns the axles to move the car.
Additionally, some electric cars are equipped with regenerative braking systems, which capture the energy released when the brakes are applied and use it to recharge the batteries.
The Future of Electric Cars
Electric cars have become increasingly popular over the past decade as advances in technology have made them a viable option for many people. But how exactly do electric cars work? Electric cars are powered by electric motors instead of internal combustion engines. These motors convert electricity, either from an onboard battery or from a charger, into mechanical energy to power the car.
The electricity is stored in a high-voltage battery, which is typically lithium-ion. This battery powers the electric motor, which then drives the car’s wheels. Electric cars have several advantages over traditional fossil fuel-powered cars.
For starters, electric cars are more efficient. They convert more of the energy stored in the battery into power that can be used to move the car. This means that electric cars use less fuel than gasoline-powered cars.
Additionally, electric cars have fewer moving parts, which means they require less maintenance and are generally more reliable. Electric cars also produce fewer emissions than traditional cars. When electric cars are powered by renewable energy sources, like solar or wind power, they produce no emissions at all.
This means that electric cars are a great way to reduce your carbon footprint. Electric cars are also generally quiet and have instant torque, meaning they can accelerate quickly. This makes them great for city driving, as they can easily maneuver through traffic.
Plus, electric cars use regenerative braking, which captures energy from the brakes and stores it in the battery, which helps increase the car’s range. Overall, electric cars are a great option for those looking to reduce their environmental impact and save money on fuel. With advances in technology, electric cars are becoming more and more efficient and reliable, making them an increasingly attractive option for drivers.
The Benefits of Electric Cars
Electric cars are becoming more popular with each passing day, and for good reason. With their lower emissions, increased efficiency, and lower running costs, electric cars are becoming an attractive and viable option for many drivers. But what exactly are electric cars, and how do they work? To understand this, it’s important to look at the components that make up an electric vehicle.
The primary components of an electric car are the electric motor, battery, and controller. The electric motor converts the electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy, propelling the vehicle forward. The battery is a rechargeable unit that stores energy from an external source, like a wall outlet or solar panel and supplies power to the motor.
The controller regulates the amount of power from the battery that goes to the motor, allowing the driver to control the speed and torque of the vehicle. By using these components together, electric cars are able to provide a more efficient and cleaner form of transportation.
The Challenges Facing Electric Cars
The electric car has come a long way in recent years, but there are still some challenges that need to be overcome before it becomes the preferred mode of transportation. One of the challenges is understanding exactly how electric cars work. While the basics of electric cars are relatively simple, there are a number of complex factors that come into play when it comes to powering and controlling an electric vehicle.
Learning how electric cars function can help us to understand better the challenges that must be addressed in order to make them more widely accessible.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do electric cars work?
Electric cars are powered by batteries, which store electricity. The electricity is then used to power an electric motor, which turns the wheels and propels the car forward.
What are the advantages of electric cars?
Electric cars are more efficient, cost less to run, and produce no emissions. They also require less maintenance and offer a smoother and quieter driving experience compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars.
What are the key components of an electric car?
The key components of an electric car include the electric motor, batteries, a controller, and a charging port. The electric motor is powered by the batteries, which the controller manages, and the charging port allows the car to be recharged when needed.
How does the battery in an electric car work?
The battery in an electric car stores and releases energy to power the car’s motor. Most electric cars use lithium-ion batteries, which are lightweight and efficient. The batteries are recharged by plugging the car into an electric outlet or through regenerative braking, which converts energy from braking into electricity.
How is an electric car charged?
Electric cars are typically charged by plugging them into an electric outlet or a charging station. The battery is recharged by drawing electricity from the power source and storing it for later use.
What is regenerative braking?
Regenerative braking is a feature in electric cars that allows the motor to reverse and convert the energy generated from braking into electricity. This energy is then stored in the battery, helping to recharge it and extend the car’s range
Conclusion
Electric cars are an efficient way to get around, and with the advancements in battery technology, they’re only getting better! With their low emissions and minimal maintenance costs, electric cars are quickly becoming the preferred method of transportation in the future. So, the answer to how do electric cars work is simple – by taking advantage of the power of electricity!

I am James Beaupre, the founder of batteryvehicleprice.com. With a deep-rooted passion for vehicle batteries, I have dedicated my career to exploring and understanding the intricacies of this crucial technology. My website aims to provide valuable insights and information on battery-powered vehicles, empowering individuals to make informed decisions.
